Biological Products:
Bioaugmentation products for Wastewater applications in Papermills, Refineries, Chemical, Tanneries, Municipalities, Textiles, Steel, Agriculture, Animal feedlot, Gun Powder plant, Food and Beverage- Dairy Products, Orange Juice factory, Wineries, Cookie factory, Vegetable processing plant, Meat packing, Barbecue Restaurant, Aquaculture, Ornamental Ponds with algae , CAFO, Nursing homes, Military, Campgrounds, Universities, Regulatory agencies, River and Lake remediation
Lab Services:
Filamentous Identification Lab Service. One reason to identify filaments is to determine the filaments characteristics and then determine the type present. If the type is found out, a root cause can usually be associated with a particular filament. If the cause is known, then a correction can be made to alleviate problems. Chlorination is only a quick fix. Without process changes, filaments will grow back after chlorination. Wastewater Biomass Analyses and Cooling Tower Analyses also available
Training Materials:
Training is an integral part of any job. Not everyone is at the same level of training. Many people want beginning concepts and basics. Some need technical information or troubleshooting. Some want equipment, technology or process information. We have developed a full set of Basic training, Advanced training, Filamentous Identification the Easy Way as well as custom training CD's Manuals. We also provide hands-on training classes and soon will have an Online "E-University".
|
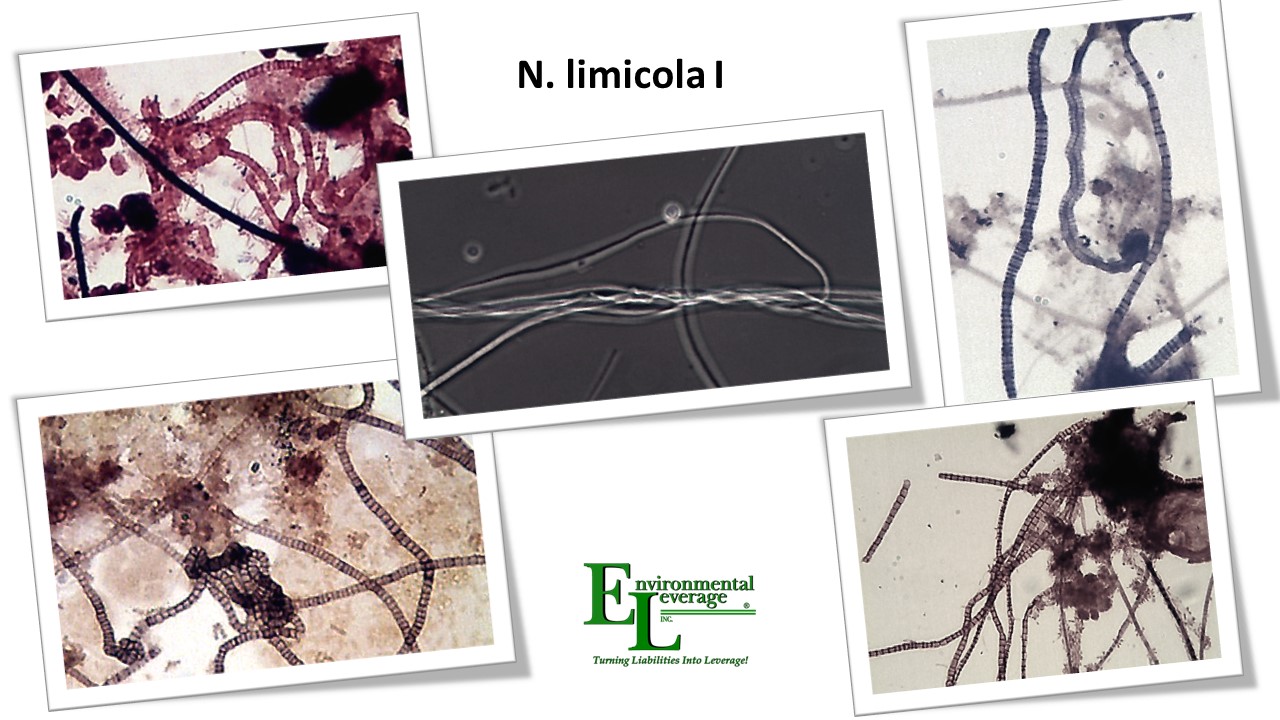
N. limicola I
Latest News!
We hope you like the new look of our Filamentous Bacteria Identification Pages If you would like more information on filaments, you might want to consider purchasing our Filamentous Identification the Easy Way Training materials. We also have our lab that can perform a Filamentous identification lab analyses of your own MLSS for more information The album above has N limicola I as well as N limicola II photos. Both are similar and have the same causes and controls
Nostocoida Limicola I What really is this called? We have heard many species now depending upon who's text book you look at. With all the DNA probes, FISH analyses, it becomes confusing as to what is the name of each filament.
When trying to determine species, stick to the basics, and focus on the causes and controls of the filaments present. The main point of any filamentous identification is not to get a PhD, but to fix your plant!
Identification Medium length , non-motile filaments (100-200 µm). Bent and irregularly coiled filaments with incidental true branching. Knots sometimes seen. Cell septa are clear with indentations. Cells are oval or disc shaped (1.2-1.4 µm). Filaments are found within the floc structure but may occur in the bulk solution. The filament staining is variable, it is usually Gram negative but sometimes positive and Neisser positive. Usually easy to identify due to its Neisser staining properties. Stains entirely purple and looks like stacked discs (or hockey pucks). In industrial wastes, an organism that is Gram negative and Neisser negative occurs. There is no sheath and there are no sulfur granules. Poly-ß-hydroxybutric acid (PHB) granules are frequently observed as dark intracellular granules. Attached growth is usually uncommon.
Similar Organisms: Three subtypes are known. Similar to N limicola I also. Resembles M. parvicella or Type 021N except in its Neisser staining properties.
Environment This filament is usually found in environments where there is low D.O. or septicity. Often found with low nutrients and the presence of organic wastes. Wastes containing starch seem more selective to this filament. Bulking is more common in industrial wastes. The filament appears to be facultative fermentative, which is unique for most filaments. We see this quite often in Chemical, Refineries and Steel mill facilities. Often found when activated carbon is present.
Control: Check solids handling, check D.O. We have never seen this filament as a dominant species. Usually is found in low to common levels except in Industry with high septicity. Check nutrients, especially phosphorus.
Rank: N. limicola ranks 12th in number of predominance in industry. Typically not found in kraft mills. Common in municipalities. If you have a hard time identifying whether it is N limicola I or II does it really matter when both filaments are due to the same cause and process control. The whole point of filamentous identification is to find a solution to help your facility run better so make it easy on yourself.
For more information on Filamentous Identification More photos to come. . .
If you need more information on our Filamentous Identification the Easy Way Training CD or on Internet training on Filamentous bacteria, causes and controls How and why on Wastewater Biomass Analyses Wastewater Bioaumgentation Products
|