Biological Products:
Bioaugmentation products for Wastewater applications in Papermills, Refineries, Chemical, Tanneries, Municipalities, Textiles, Steel, Agriculture, Animal feedlot, Gun Powder plant, Food and Beverage- Dairy Products, Orange Juice factory, Wineries, Cookie factory, Vegetable processing plant, Meat packing, Barbecue Restaurant, Aquaculture, Ornamental Ponds with algae , CAFO, Nursing homes, Military, Campgrounds, Universities, Regulatory agencies, River and Lake remediation
Lab Services:
Filamentous Identification Lab Service. One reason to identify filaments is to determine the filaments characteristics and then determine the type present. If the type is found out, a root cause can usually be associated with a particular filament. If the cause is known, then a correction can be made to alleviate problems. Chlorination is only a quick fix. Without process changes, filaments will grow back after chlorination. Wastewater Biomass Analyses and Cooling Tower Analyses also available
Training Materials:
Training is an integral part of any job. Not everyone is at the same level of training. Many people want beginning concepts and basics. Some need technical information or troubleshooting. Some want equipment, technology or process information. We have developed a full set of Basic training, Advanced training, Filamentous Identification the Easy Way as well as custom training CD's Manuals. We also provide hands-on training classes and soon will have an Online "E-University".
|
The "Critical 5"plus oneLatest News!
What's New!
We have just added "Virtual Audits" to our capabilities. Check out our new Services. We are in the process of developing new courses for our ""Online E-University" in order to meet the needs of our global customers that cannot travel to our public classes.Visit our new website www.WastewaterElearning.com/Elearning
Ok, so what exactly are the "Critical 5 plus one"? I have never heard of that. There are 5 critical measurements that should be monitored and controlled to effectively run a biological treatment plant efficiently; Temperature, Dissolved Oxygen, Ammonia, Ortho-phosphate and pH.
Acceptable Environmental Parameters for Biological Activity: There are 5 critical measurements that should be monitored and controlled to effectively run a biological treatment plant efficiently; Temperature, Dissolved Oxygen, Ammonia, Ortho-phosphate and pH.
PARAMETER
ACCEPTABLE
OPTIMUM
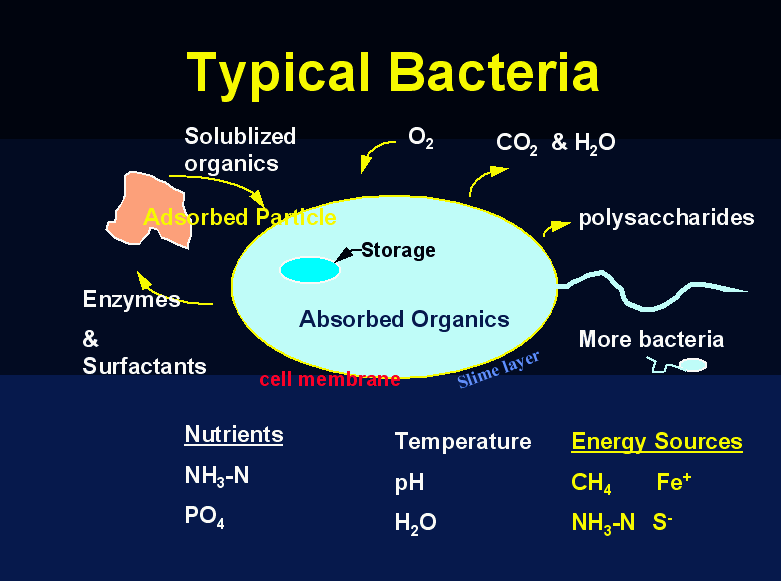
As silly as these may seem or appear to be just general information, they are extremely critical. 90% of all audits we conduct have at least one or more of these parameters in the wrong range. These are the easiest parameters to control at your wastewater treatment plant and some of the most critical ones. The bacteria do not care about any tests you perform, (i.e. sludge judge, MLSS, F/M etc.) parameters you measure or implement as long as these Critical 5 are in the correct range. Biomass quality and final effluent results will be impacted.
Alkalinity is sometimes considered the plus one but only for plants that require the additional step on Nitrification.
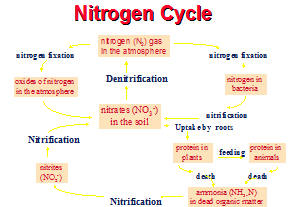
Nitrification Nitrification is a sensitive process that must coexist with the carbonaceous BOD removal process. There are many stresses that can adversely impact nitrification before the BOD or TSS removal efficiencies are affected. Biocides that are used in the cooling towers can contain chemicals that are toxic to nitrifiers. Gluteraldehyde is very toxic to nitrifiers and it tends to stay in the activated sludge. It is absorbed by the biomass. Zinc can also be toxic to nitrifiers. Alkalinity and pH were low at this time. Alkalinity is critical to Nitrification. Nitrifying bacteria
As ammonia is removed it is transformed-For each 1 gram of NH3-N oxidized to NO3, 0.15 grams of new bacteria cells are formed. Most of the NH3-N is used as an energy source. It is used in a non-assimilative way so only a small amount of biomass (sludge) is produced. Nitrification occurs 3-4 times slower than carbonaceous oxidation. Carbon dioxide (CO2) or carbonate is used as the carbon source in nitrification. 4.5 parts of O2 is needed for every part of NH3 to be degraded.
First Conversion (Ammonium to Nitrite)
Second Conversion (Nitrite to Nitrate) There is a wide range in the reported pH optima (PH 6.5 to 8.6). Typical refineries run in higher pH- `8.0-9.5. However, there is general agreement that as the pH shifts to the acid range, the rate of nitrification declines, thus, it is important that sufficient alkalinity is present in the wastewater to prevent a significant decline in the pH. It is recommended that a residual alkalinity of 50 mg/l for aeration and at least 150 mg/l for high purity oxygen systems be maintained for pH control during nitrification. Low pH conditions are only inhibitory and not toxic toward nitrifiers. Caustic or lime addition may be required to supplement low alkaline wastewaters.
Calculations on alkalinity must be considered using the fact that amines are also present in the water and will degrade down to release some of the ammonia for use in nitrification. Targeting alkalinity must include free ammonia as well as bound ammonia for final degradation rates to achieve below 1 in the system.
Contact us on any questions you may have on the Critical 5 parameters at admin@EnvironmentalLeverage.com or 630-906-9791
Back to Troubleshooting tips and Newsletters
|

 Cold
weather can sometimes be a problem for many plants due to permit
restrictions and decreased biological activity. Many plants experience a
significant drop in biological activity due to the temperature levels
decreasing. Biological activity drops one log level for each 10-degree drop
in temperature. This can significantly impact the amount of BOD loading that
the biomass can handle effectively.
Cold
weather can sometimes be a problem for many plants due to permit
restrictions and decreased biological activity. Many plants experience a
significant drop in biological activity due to the temperature levels
decreasing. Biological activity drops one log level for each 10-degree drop
in temperature. This can significantly impact the amount of BOD loading that
the biomass can handle effectively.