Biological Products:
Bioaugmentation products for Wastewater applications in Papermills, Refineries, Chemical, Tanneries, Municipalities, Textiles, Steel, Agriculture, Animal feedlot, Gun Powder plant, Food and Beverage- Dairy Products, Orange Juice factory, Wineries, Cookie factory, Vegetable processing plant, Meat packing, Barbecue Restaurant, Aquaculture, Ornamental Ponds for algae control, CAFO, Nursing homes, Military, Campgrounds, Universities, Regulatory agencies
Lab Services:
Filamentous Identification Lab Service. One reason to identify filaments is to determine the filaments characteristics and then determine the type present. If the type is found out, a root cause can usually be associated with a particular filament. If the cause is known, then a correction can be made to alleviate problems. Chlorination is only a quick fix. Without process changes, filaments will grow back after chlorination. Wastewater Biomass Analyses and Cooling Tower Analyses also available
Training Materials:
Training is an integral part of any job. Not everyone is at the same level of training. Many people want beginning concepts and basics. Some need technical information or troubleshooting. Some want equipment, technology or process information. We have developed a full set of Basic training, Advanced training, Filamentous Identification the Easy Way as well as custom training CD's Manuals. We also provide hands-on training classes and soon will have an Online "E-University".
Audits and Consulting:
At Environmental Leverage® Inc., we have a team of experienced individuals who come into your plant with a fresh pair of eyes. The system is checked from influent to effluent. System optimization, equipment efficiency and operational excellence are key components explored. Key Benefits Equipment efficiency Total Cost of Operation reductions Reliability and safety An onsite audit is conducted to examine system parameters, process controls, and current monitor and control procedures. A physical walk-through is conducted, process flow diagrams are examined, previous design criteria are examined and current standard operating procedures are evaluated along with data logs.
|
Filamentous Identification-What is in a nameLatest News!
What's New!
We have just added "Virtual Audits" to our capabilities. Check out our new Services. We are in the process of developing new courses for our ""Online E-University" in order to meet the needs of our global customers that cannot travel to our public classes.Visit our new website www.WastewaterElearning.com/Elearning
What's in a name and
ID?
There are now a group of organisms that in the past were all lumped together during a filamentous identification. Newer testing exists such as FISH and DNA sequencing, are getting more and more technical. Nocardia pinensis can been changed to Skermania piniformis.Nocardia amarae has recently been reclassified as Gordona amarae Some Nocardia
have been classified as
Actinomycetes
Are you getting confused yet?Is it really critical in wastewater? Do you need a PhD to figure it all out? Does it matter and how is it going to help you with solving your problems at your plant? We have listed a few names below that have changed. For the purpose of this book, we are going to stick with Nocardia as branching filaments- gram positive that cause foaming and bulking. We have seen tons of different types of "Nocardia". Guess what, they all are usually caused by the same thing and the process controls are the same. Our goal is not to be so overly technical, but to help you solve a problem in your plant. You do not really win any awards if you get the absolute correct name. You just probably spent a lot of time studying it and getting "technical" Let's get back to solving the problems in the wastewater treatment plant. If the naming systems change significantly, the characteristics or causes and controls are meaningful, we will most certainly update our books, websites and photos. At this point, we are trying to stick with the title, Filamentous ID for dummies, not Ph.D. masters! So hopefully, you are not upset or feel like the technical information is incorrect. Read the
sections below if you want to get technical.
If not, skip to the next sections and enjoy!!
NALO or
GALO Nocardia
pinensis
Notice how the gram staining is more variable. Neisser staining is slightly different than the traditional Nocardia like organisms also, Neisser is more variable with dark purple spots in similar sections.
1000x Gram stain
PTLO
"Actinomycetes" These are gram
positive branched rods without the distinctive branching patterns of NALO
and Skermania piniformis. This category includes coryneform bacteria. These
are members of the
You can see on this Neisser stain below, three different species of "Nocardia" in the same sample
200x Phase contrast Actinomycetes-right What is interesting though, is they all cause foaming in a wastewater treatment plant. Process changes are very similar and do not change from species to species, only if the cause is different.
1000x Neisser Stain Nocardia forms three types
These filaments may be found in environments where there is low F/M (0.08-0.35 lbs BOD) and with a long MCRT (10-40 days). Usually high wastewater grease, oil and fat content are the main cause. They are found more commonly in the warmer temperatures.
There are definitely more than one species of Type 021N as we have shown you in our own photos. Thiothrix now has many species. Leucothrix is typically
a marine species, but is getting mention in wastewater environments lately.
1000x Gram stain Filament similar to 0041 but with false branching
N limicola has many different looks. Here is one version where the filament is basically gram variable, most of it negative, but the distinguishing features of the cell shape, septa and some Neisser negative still make it easy to tell this is a form of N. Limicola. 1000x Neisser Stain N. limcola two strains.
There are numerous debates on N limicola III vs. Isosphaera and even which filament is N limicola III
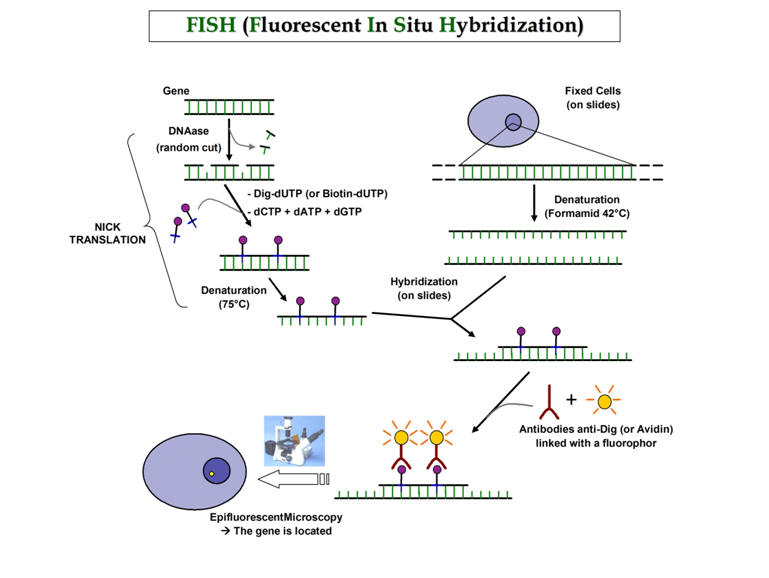
Now we have even another way to make it harder and more confusing for normal lab personnel and operators to identify filaments. FISH- Fluorescent in situ Hybridization
How many organisms of the same Type with slight DNA changes determines a new “species”
It seems every PhD researcher is trying to build a name by creating "new species" The 15 Eikelboom type 021N bacteria that were investigated were divided into three distinct groups (I to III) on the basis of their genotypic and phenotypic characteristics. The creation of two novel species is proposed, Thiothrix disciformis sp. nov. for the group I strains (type strain B3-1(T)=JCM 11364(T)=DSM 14473(T)) and Thiothrix flexilis sp. nov. for the group III strains (type strain EJ2M-B(T)=JCM 11135(T)=DSM 14609(T)).
Stick to “groupings”
Group the filament types by causes and control The main point in a filamentous identification is not to obtain a PhD but to fix your wwtp! There are only so many causes and controls -Work on problem solving
For more information on Filamentous Identification
If you need more information on our ©Filamentous Identification the Easy Way™ Training CD or on Internet training on Filamentous bacteria, causes and controls How and why on Wastewater Biomass Analyses
|

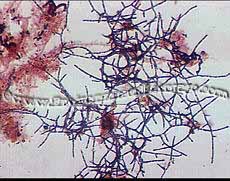
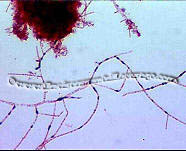
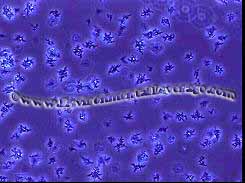

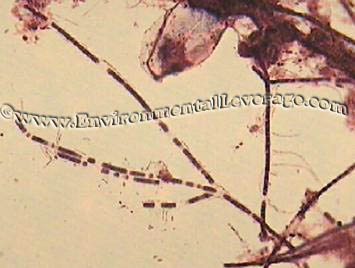 Some
studies don't differentiate between Types 0041 and 0675.
We have seen a type of 0041 that is branching and fits no current
descriptions, yet fits with causes and controls.
Some
studies don't differentiate between Types 0041 and 0675.
We have seen a type of 0041 that is branching and fits no current
descriptions, yet fits with causes and controls.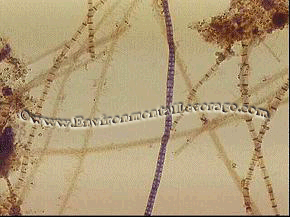 Leptothrix,
which is a typical inhabitant of metal-rich streams
Leptothrix,
which is a typical inhabitant of metal-rich streams